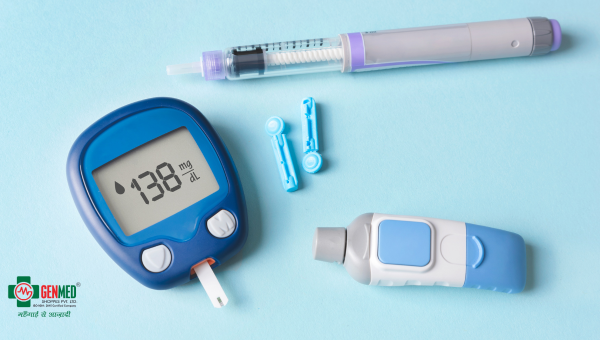
Understanding Glucometers: Your Guide to Blood Sugar Monitoring
Jan 17, 2025
Accurate blood sugar monitoring is essential for managing diabetes. Keeping blood sugar levels in check can help prevent complications and improve quality of life. Understanding how glucometers work and their various types can empower individuals to effectively monitor their health.
The Rising Prevalence of Diabetes
Diabetes is becoming more common, affecting millions worldwide. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), around 422 million people had diabetes in 2014, and these numbers have only risen. This growing issue emphasizes the need for effective monitoring tools like glucometers.
The Importance of Early Detection and Management
Early detection of high blood sugar levels can make a significant difference. It allows for timely intervention and personalized management plans, reducing the risk of complications such as heart disease, kidney damage, and nerve issues. Regular monitoring is crucial in catching these problems before they worsen.
Glucometers: Your Partner in Diabetes Care
A glucometer is a device that measures blood glucose levels. By using a glucometer, individuals can take control of their health. It provides valuable insights into daily blood sugar patterns, helping to manage diet, medication, and lifestyle choices.
Types of Glucometers: Finding the Right Fit
Choosing the right glucometer is essential to effective diabetes management. Different types offer various features that cater to individual needs.
Finger-Stick Glucometers: The Traditional Approach
Finger-stick glucometers are classic options. These devices require a small blood sample from your fingertip to provide a reading.
Accuracy and Reliability of Finger-Stick Devices
These devices are known for their accuracy when used correctly. Proper calibration and technique can yield reliable results.
Pros and Cons of Traditional Glucometers
-
Pros:
-
Generally lower cost
-
Easy to find and use
-
Quick readings
-
-
Cons:
-
Requires finger pricks
-
May be painful for some users
-
Can be difficult to monitor trends over time
-
Continuous Glucose Monitors (CGMs): Real-Time Monitoring
CGMs offer real-time insights. These devices continuously check blood sugar levels without the need for finger pricks.
How CGMs Work and Their Benefits
CGMs use a small sensor placed under the skin to track glucose levels throughout the day. They provide alerts when levels are too high or low, allowing for immediate action.
Limitations and Considerations of CGMs
-
Pros:
-
Continuous monitoring
-
Reduces finger pricks
-
Provides trend data and alerts
-
-
Cons:
-
Higher cost
-
Requires regular sensor replacement
-
May not be as accurate during rapid changes in glucose
-
Flash Glucose Monitors: A Blend of Convenience and Accuracy
Flash glucose monitors combine features of both CGMs and traditional devices. They allow users to scan a sensor to get real-time glucose readings without continuous monitoring.
Understanding Flash Glucose Monitor Technology
These devices require a sensor typically worn on the arm. By scanning the sensor with a reader or smartphone, users can see their current glucose levels.
Comparing Flash Monitors to CGMs and Traditional Glucometers
-
Flash Monitors:
-
Convenient scanning
-
No need for constant wear
-
Offers trend data
-
How to Use a Glucometer: A Step-by-Step Guide
Using a glucometer accurately is important for reliable results. Follow these steps to ensure proper usage.
Preparing for a Blood Glucose Test
Gathering Necessary Supplies
You'll need:
-
Glucometer
-
Test strips
-
Lancing device
-
Alcohol swabs (optional)
Proper Handwashing Technique
Wash your hands thoroughly with soap and water. This helps prevent contamination and ensures a more accurate reading.
Performing the Test: A Detailed Procedure
Inserting the Test Strip
Insert a new test strip into the glucometer. Wait for the device to be ready.
Applying the Blood Sample
Use a lancing device to prick the side of your fingertip. Apply a drop of blood to the test strip and wait for the reading.
Interpreting Your Results: Understanding Blood Sugar Levels
Blood sugar levels are measured in milligrams per deciliter (mg/dL). The typical ranges are:
-
Normal: 70-99 mg/dL
-
Pre-diabetes: 100-125 mg/dL
-
Diabetes: 126 mg/dL or higher
Accuracy and Reliability of Glucometer Readings
Accuracy is crucial when monitoring blood sugar. Several factors can impact the readings.
Factors Affecting Glucometer Accuracy
Calibration and Maintenance of Devices
Regular calibration ensures your glucometer gives precise readings. Follow manufacturer guidelines for calibration.
Impact of Test Strip Storage and Expiration
Check expiration dates on test strips. Store them in a cool, dry place to maintain their effectiveness.
Ensuring Reliable Results: Best Practices
-
Always wash hands before testing.
-
Use fresh test strips.
-
Follow the manufacturer's instructions carefully.
Maintaining Your Glucometer: Tips and Best Practices
Regular maintenance will keep your glucometer functioning well and providing accurate results.
Cleaning and Storage of Your Glucometer
Proper Handling and Prevention of Damage
Store your glucometer in a protective case. Keep it away from extreme temperatures and moisture.
Regular Maintenance Schedule
Check your glucometer regularly for signs of damage. Clean it gently with a soft cloth as needed.
Calibrating Your Glucometer for Optimal Accuracy
Frequency of Calibration
Calibrate your glucometer as recommended by the manufacturer, usually before the first use and periodically after.
Steps Involved in Calibration
Follow the specific calibration steps outlined in the user manual. This may include using control solutions.
Replacing Test Strips and Batteries
Storage and Expiration Dates of Test Strips
Keep test strips in their original container. Check the expiration date before use.
Identifying Signs of Battery Depletion
Replace batteries when the device shows low battery indications to ensure accurate readings.
Choosing the Right Glucometer for Your Needs
Selecting a suitable glucometer can enhance your diabetes management process.
Factors to Consider When Selecting a Glucometer
Cost and Insurance Coverage
Consider your budget and if your insurance covers the device. Prices can vary widely.
Features and Functionality
Look for features that suit your lifestyle, such as Bluetooth connectivity or memory storage.
Consulting with Healthcare Professionals
Recommendations Based on Individual Needs
Talk with your doctor or diabetes educator for personalized recommendations. They can suggest the right device for your situation.
Importance of Personalized Guidance
Every individual’s needs vary. Professional advice ensures you're making the best choice for your health.
Conclusion: Empowering Yourself Through Blood Sugar Monitoring
Understanding and using a glucometer effectively can enhance your life and health.
Key Takeaways: Main Points to Remember
-
Regular monitoring helps maintain blood sugar levels.
-
Different types of glucometers offer various advantages.
-
Consult with healthcare professionals for guidance.
Importance of Regular Blood Sugar Monitoring
Regular monitoring is essential for managing diabetes and preventing complications.
Seeking Professional Guidance for Optimal Diabetes Management
Take control of your health. Regular check-ins with your healthcare provider contribute to better management and educational resources.
Recent Post

The Importance of Daily Nutrition : Are You Getting Enough?

The Ultimate Guide to Baby Care: Expert Tips and Essential Advice
Human Metapneumovirus (HMPV)

Men caring for others is a topic that is often overlooked or minimized in discussions about gender roles and expectations.

Unleash the Power of Neem: Unveiling its Ayurvedic Benefits

Vitamin E Capsules for Hair: Benefits
Understanding Infectious Diseases

Generic medicines offer the same therapeutic benefits as their brand-name counterparts but at a lower cost, making them more accessible to patients while maintaining safety and efficacy.

Allergies Are Common Problem in People
Mastering Diabetes Care - Your Guide to a Healthier Life